I. Understanding Electric Fan Heaters: Working Principle and Core Advantages
The Basic Definition and Working Mechanism of Electric Fan Heaters
Electric Fan Heaters, commonly referred to as Space Heaters, are popular, highly portable devices designed for localized heating. Their core design principle is to convert electrical energy into heat, and then use a fan to quickly and effectively push that warm air into a room to achieve rapid heating.
A typical Electric Fan Heater consists of the following key components:
- Heating Element: This is the part that converts electrical energy into thermal energy, which can be an exposed metal coil, insulated mica boards, or modern Ceramic elements.
- Fan: Responsible for forcibly circulating air over the heating element. Unlike natural convection heaters, the inclusion of a fan significantly increases the speed and efficiency of heat transfer.
- Safety and Control System: Includes crucial entities such as the Thermostat, Overheat Protection, and Tip-Over Switch.
Working Mechanism:
When the power is turned on, current flows through the heating element, generating heat according to Joule's law. Subsequently, the built-in fan activates, drawing cold ambient air into the unit and forcing it to pass over the high-temperature heating element. Once heated, the air is forcefully blown out by the fan, rapidly circulating within the localized space. This forced air delivery mechanism is the key feature that distinguishes Electric Fan Heaters from other electric heating devices, enabling a much quicker rise in temperature.
Advantages of Electric Fan Heaters Compared to Central Heating
Electric Fan Heaters are favored by users worldwide because they offer a range of practical benefits that traditional central heating systems often cannot match.
Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd., a leading manufacturer of small household appliances headquartered in Cixi (China's appliance capital), has been committed to delivering high-quality heating products since 2007. Leveraging our advanced manufacturing capabilities and strategic location near Ningbo Port, Shanghai, and Hangzhou, we integrate reliability, innovation, and efficiency into our designs. We ensure our products excel in key areas to meet diverse user demands:
| Feature |
Advantage of Electric Fan Heaters |
Limitation of Central Heating Systems |
| Startup Speed |
Quick Heating: Provides warmth almost instantly, without waiting for pipes or ventilation systems to preheat. |
Slow to warm up, requiring time for the entire system or house structure to reach the target temperature. |
| Cost Efficiency |
Cost-Effectiveness: Low initial purchase price, and heats only the area in use, avoiding unnecessary energy consumption. |
High initial installation costs, and high energy consumption as it heats the entire house during operation. |
| Flexibility |
Portability: Easy to move between rooms for “zone heating” or “supplementary heating.” |
Fixed installation; cannot be moved, only suitable for whole-house heating. |
The Primary Benefits of Electric Fan Heaters
1. Excellent Portability and Flexibility:
This is one of the most significant advantages of Electric Fan Heaters. They are typically compact, feature carry handles, and can be easily moved from the living room to the bedroom, or even to a garage or basement. This ability for on-demand heating allows users to precisely control heat distribution based on their activity zones throughout the day.
2. Quick Heating:
Due to the forced air delivery, warmth from Electric Fan Heaters is felt almost immediately. This rapid response is crucial for users who need to quickly warm up a bathroom in the morning or heat a temporary workspace.
3. Cost-Effectiveness:
Compared to the expensive upgrades of central heating systems or the high operating costs of gas heating, the initial investment in an efficient Electric Fan Heater is significantly lower. Furthermore, by only heating the room currently being used, users can dramatically reduce their overall energy consumption and electricity bills.
4. Enhanced Safety Features:
Modern Electric Fan Heaters prioritize safety. Products developed by companies like Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd. integrate multiple key safety mechanisms, backed by stringent quality control and robust R&D, including:
- Overheat Protection: Automatically shuts off the power when internal component temperatures exceed a preset safe threshold.
- Tip-Over Switch: Immediately cuts the power when the unit is accidentally knocked over or tilted, greatly mitigating fire risk.
II. In-Depth Analysis of Electric Fan Heater Types
Understanding the main heating technologies available is vital before selecting the right Electric Fan Heater. While all types use a fan to distribute heat, differences in their heating elements and operational methods determine their suitable environment and energy efficiency. As a manufacturer located in the appliance capital of Cixi, Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd. offers various Electric Fan Heaters utilizing different technologies to meet the diverse supplementary heating needs of customers worldwide.
1. Ceramic Fan Heaters:
Ceramic Fan Heaters are among the most popular Electric Fan Heater types today, particularly valued for their superior safety and energy efficiency.
- Working Principle:
These heaters use PTC (Positive Temperature Coefficient) Ceramic plates as the main heating element. When current flows through the ceramic plates, heat is generated, and the fan then blows air over these hot plates, distributing the warmth.
- Entity Explanation: The unique aspect of the Ceramic element is its self-regulating temperature property. Once the ceramic plate reaches a specific temperature, its electrical resistance increases dramatically, automatically limiting the current and power output, preventing continuous overheating.
- Pros:
- Energy Efficient: Possesses self-regulating capability, automatically reducing power consumption once the target temperature is reached.
- High Safety: Ceramic elements do not glow red like metal coils, reducing the risk of burns and fire.
- Stable Heat: Output heat is uniform and continuous.
- Cons:
- Initial purchase cost is usually higher than traditional coil heaters.
- Generally best suited for small to medium-sized rooms; less effective in large, open spaces.
- Use Cases: Offices, bedrooms, personal workstations, and other areas requiring safe and stable heating.
2. Convection Fan Heaters:
Convection heaters utilize the natural circulation of air to warm a room, with the fan's addition significantly accelerating this process and improving the uniformity of heat distribution.
- Working Principle:
These Electric Fan Heaters use exposed or insulated metal coils or elements to heat the air. As the element heats the air, the built-in fan pushes the warm air into the room; this air rises, and cooler air is drawn into the bottom of the heater, creating an accelerated convection cycle to eventually achieve uniform room heating.
- Pros:
- Good for even heat distribution: Excellent for prolonged operation to steadily raise the temperature of an entire room.
- Generally provides a continuous and gentle sense of warmth.
- Cons:
- Heating speed is slower (Can take longer to heat up) compared to ceramic or infrared models, requiring time to notice a significant temperature change.
- Use Cases: Living rooms and larger, enclosed areas that require widespread temperature increase.
3. Infrared Fan Heaters:
Infrared heaters operate fundamentally differently from the other two types, providing radiant heat by mimicking the warmth of the sun.
- Working Principle:
These heaters generate Infrared Radiation through special quartz or metal elements. This radiation passes directly through the air to heat objects and people in its path, rather than heating the air itself. The fan is often included to help dissipate heat from the element or to assist in uniformly moving the radiant heat into a localized area.
- Pros:
- Efficient: As they do not heat the air, heat loss is minimal, and warmth is felt almost immediately upon activation.
- Heats objects, not air: Ideal for use in drafty or ventilated environments.
- Cons:
- Heat is directional: If the user moves out of the radiation path, the feeling of warmth quickly diminishes.
- Limited coverage area; not ideal as a general heating device for large spaces.
- Use Cases: Garages, covered patios, and workstations that require precise, quick, and directional heating.
Key Type Comparison Table:
The table below summarizes the differences in performance entities among the three main Electric Fan Heater types:
| Feature |
Ceramic Type |
Convection Type |
Infrared Type |
| Heating Medium |
Ceramic Element (PTC) |
Metal Coil or Element |
Infrared Radiation Element |
| Heat Distribution |
Fan-forced Convection |
Fan-accelerated Convection Circulation |
Direct Radiant Heating of Objects |
| Heating Speed |
Fast |
Slower |
Extremely Fast (Instant sensation) |
| Energy Efficiency |
Higher (Self-regulating) |
Average |
High (for localized heating) |
| Safety |
Very High (Cool-Touch Housing) |
Medium (Element may be exposed) |
High (Does not heat surrounding air) |
| Suitable Space |
Small to Medium Rooms |
Larger, enclosed Rooms |
Localized, Directional Areas |
III. Key Features to Consider When Buying an Electric Fan Heater
Choosing the most suitable Electric Fan Heater requires a comprehensive evaluation of its heating capacity, safety features, energy efficiency, and operational convenience. Deepening your understanding of the following core entities and technical specifications will help you make a well-informed investment decision.
1. Heating Capacity and Wattage
Heating capacity is the primary metric for evaluating an Electric Fan Heater's performance. It determines the size of the area the unit can effectively heat and the speed at which it can raise the temperature.
- Wattage: This is the most direct measure of an electric heater's power. Wattage represents the amount of electrical energy the unit consumes per hour during operation. For household Electric Fan Heaters, common wattage ranges from 750 Watts to 1500 Watts.
- BTU (British Thermal Unit): While BTU is more commonly used for air conditioners and gas heaters, in the electric heating field, it indicates the amount of heat the unit produces per hour. A simple conversion is: 1 Watt ≈ 3.41 BTU/h. Therefore, a standard 1500 W Electric Fan Heater provides approximately 5115 BTU of heat.
Room Size and Wattage Matching Recommendations:
Selecting the correct Wattage is crucial. Power that is too low will fail to achieve the desired heating effect; power that is too high may lead to wasted energy or circuit overload.
| Room Area (Feet²) |
Room Area (Meters²) |
Recommended Minimum Wattage |
Recommended Minimum BTU/h |
Notes |
| 100 |
≈ 9.3 |
750 W |
≈ 2557 |
Suitable for personal workspaces or small bedrooms |
| 150 |
≈ 14 |
1000 W |
≈ 3412 |
Suitable for medium bedrooms or offices |
| 200 |
≈ 18.6 |
1250 W |
≈ 4265 |
Suitable for larger bedrooms or small living rooms |
| 250 |
≈ 23.2 |
1500 W |
≈ 5118 |
Suitable for auxiliary heating in living rooms or open areas |
2. Essential Safety Features
Given that Electric Fan Heaters involve high temperatures and electricity, safety is a non-negotiable factor in any purchasing decision. Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd. consistently places strict safety standards at the core of product design to ensure safe use for customers globally.
- Overheat Protection: This is a required safety entity. When the unit's internal components (such as the heating element or circuit board) reach an unsafe temperature, the built-in temperature sensor will immediately trigger an automatic shut-off mechanism, preventing internal damage and fire risks.
- Tip-Over Switch: This function ensures that if the Electric Fan Heater is accidentally knocked over or tilted past a certain angle, the power is instantaneously cut off. This is particularly important for households with pets or children.
- Cool-Touch Housing: Especially for ceramic heaters, the exterior casing is designed with special materials to ensure that external touch areas remain cool during operation. This significantly reduces the risk of accidental burns.
- Automatic Delay Shut-Off: Some high-end models feature a cooling cycle before powering down completely, which protects internal components and extends the unit's lifespan.
3. Energy Efficiency and Running Costs
While all electric heaters convert 100% of the consumed electrical energy into heat, truly efficient Electric Fan Heaters minimize unnecessary runtime through smart controls, thus achieving the goal of an Energy Efficient Heater.
- Adjustable Thermostat: Allows users to set a precise target temperature. Once the room reaches this temperature, the Thermostat automatically turns off the heating element (or switches to a low-power mode) and restarts when the temperature drops. This avoids continuous operation and is key to energy saving.
- Timer Settings: The Timer allows users to preset the unit's operation duration (e.g., run for 2 hours before bedtime), preventing energy waste from forgetting to turn the unit off.
- Energy Star Certification: Although Electric Fan Heaters rarely receive Energy Star certification (because their 100% heat conversion efficiency is fixed), in other small household appliances, Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd. is committed to enhancing efficiency, which is reflected in the precision control systems of its Electric Fan Heaters, aimed at minimizing unnecessary energy consumption.
4. Noise Level and Operational Convenience
Fan operation inevitably generates noise, but this can be controlled through design optimization.
- Decibel (dB) Rating: Look for models that provide a low Decibel rating in their specifications. For use in bedrooms, studies, or offices, models with quiet modes or advanced ceramic technology are recommended to ensure comfort.
- Controls and Settings: Easy-to-use control panels, clear digital displays, and multiple heat settings (e.g., low heat, high heat, fan-only mode) are essential. Remote Control functionality greatly enhances convenience, particularly for operation from a distance or during the night.
5. Design and Portability
- Compact Designs: The advantage of a Small Heater is its ease of movement and storage, making it ideal for limited spaces.
- Carry Handles: Integrated Carry Handles enhance Portability, allowing users to safely and easily transfer the heater between different rooms.
- Aesthetic Design: Modern homes demand that Electric Fan Heaters look stylish, with many models now featuring contemporary designs that blend seamlessly with home décor.
IV. Safety Tips and Maintenance for Electric Fan Heaters
Even when choosing a high-quality Electric Fan Heater with advanced safety features (like overheat protection and tip-over switch), such as those manufactured by Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd., users must adhere to strict operating guidelines. Correct usage and regular maintenance are crucial for preventing fire hazards, ensuring family safety, and extending the unit's lifespan.
Safety Tips for Using Electric Fan Heaters
Due to the high heat generated by Electric Fan Heaters, improper use can lead to serious safety issues. Always follow these safety rules:
- Maintain Safe Distance (Three-Foot Rule):
- Core Requirement: Always place Electric Fan Heaters at least three feet (about one meter) away from any flammable materials.
- Flammable Materials Include: Curtains, furniture, bedding, paper, clothing, carpet edges, and paint thinners. The forced hot air stream can rapidly ignite lightweight materials nearby.
- Never Leave Unattended:
- Crucial Principle: Never leave a running Electric Fan Heater unsupervised.
- Always turn off and unplug the heater when leaving the room, going to sleep, or leaving the house. While modern heaters feature overheat protection, avoiding long, unsupervised operation is the best safety practice.
- Use on a Stable Surface:
- Always place the heater on a firm, level, flat, and non-flammable surface, such as hardwood floors or tiles.
- Avoid placing the heater on high-pile carpets or unstable shelves, which prevents accidental tipping or obstruction of bottom air intakes.
- Cord and Outlet Management:
- Do not use extension cords: Electric Fan Heaters draw high wattage, and using an extension cord can cause the cord itself to overheat or melt, leading to fire. Heaters should be plugged directly into a wall outlet.
- Check Outlet Fit: Ensure the heater's plug fits tightly into the wall outlet. If the plug is loose, stop using that outlet immediately.
- Avoid routing the cord under rugs or through high-traffic areas to prevent damage or tripping hazards.
- Keep Away from Water:
- Never use the heater in bathrooms, laundry rooms, or any damp areas to prevent electrical shock hazards.
Company Commitment to Safety:
Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd. profoundly understands the importance of safety. Through rigorous quality control and testing processes at our Cixi headquarters, we ensure that every Electric Fan Heater we manufacture complies with international safety standards. We not only build in entities like the Tip-Over Switch and Overheat Protection but also advise users to combine correct usage with these features to maintain a secure heating environment.
Maintenance and Care for Electric Fan Heaters
Proper routine maintenance preserves the efficiency and extends the lifespan of your Electric Fan Heater.
- 1. Regular cleaning to remove dust:
- Before cleaning, always turn off the power, unplug the unit, and allow it to cool completely.
- Use a vacuum cleaner's brush attachment or a soft, dry cloth to regularly remove dust and lint accumulated at the air intake and output vents. Dust buildup restricts airflow, causing the unit to overheat, which triggers overheat protection and reduces efficiency.
- 2. Checking for loose connections:
- Frequently inspect the power cord and plug for any signs of wear, cuts, cracks, or discoloration. If any damage is found, immediately stop using the unit and contact the manufacturer or a professional repair service.
- 3. Filter Cleaning/Replacement (If Applicable):
- For some Electric Fan Heaters equipped with air filters (especially ceramic models), clean or replace the filter regularly according to the user manual to maintain air quality and heating efficiency.
- 4. Proper storage when not in use:
- During the off-season, store the heater in its original packaging or in a dry, cool place away from children. Avoid placing heavy objects on the unit or its power cord during storage.
V. FAQ
This section aims to address the most common user inquiries regarding the power consumption, usage limitations, and technical comparisons of Electric Fan Heaters, providing practical and fact-based information.
How much power do electric fan heaters consume
The power consumption of Electric Fan Heaters directly depends on their Wattage entity and the duration of use.
- Calculation Formula: Operating Cost (per hour) = Wattage (kW) × Electricity Price (per kWh).
- For example: For a 1500 W (i.e., 1.5 kW) heater and a local electricity price of 0.15 /kWh, the operating cost per hour is: 1.5 kW × 0.15 /kWh = 0.225 per hour.
- Energy Saving Factors: While all electric heaters have a 100% energy conversion efficiency, Electric Fan Heaters equipped with an Adjustable Thermostat are more energy-efficient. Once the room reaches the set temperature, the thermostat shuts off the heating element, using only minimal power for the fan or sensors, thereby reducing actual running costs. Choosing an Energy Efficient Heater is key to smart control, not just the heating efficiency itself.
Electric Fan Heaters can be used for primary heating throughout the winter?
- Generally Not Recommended: Electric Fan Heaters are primarily designed as Space Heaters or supplementary heating devices. They excel at quickly warming small spaces or providing extra warmth when central heating is insufficient.
- Limitations: Attempting to heat a large house or an entire home with a single Electric Fan Heater is neither feasible nor cost-effective for year-round primary heating. For primary winter heating needs, a central heating system or larger, fixed heating installations are usually more efficient and economical.
- Positioning: Electric Fan Heaters are best used as efficient, portable supplementary heat sources.
Which is safer: ceramic or traditional coil heaters?
- Ceramic Heaters are Safer: Electric Fan Heaters featuring PTC Ceramic elements are generally considered safer.
- Reasoning:
- Self-Regulating Property: Ceramic elements have built-in temperature limiting, allowing them to self-regulate power and prevent overheating.
- Surface Temperature: The surface temperature of ceramic elements is typically lower than the glowing coils of traditional metal wire heaters, combined with a Cool-Touch Housing design, this further reduces the risk of burns or igniting dust.
- In the design and manufacturing process, Ningbo Fashida Appliance Technology Co., Ltd. prioritizes advanced materials like ceramic and integrates multiple safety entities, such as the Tip-Over Switch and Overheat Protection, to offer customers greater peace of mind.
How do I calculate the BTU I need for an Electric Fan Heater?
As discussed in the Heating Capacity section, BTU (British Thermal Unit) is primarily used to measure the total required heat output.
- Quick Estimation Method: Assuming the room is well-insulated, the rule of thumb is that approximately 10 BTU/h of heat is needed per square foot (ft²).
- Formula: Required BTU/h = Room Area (ft²) × 10
- Wattage Conversion: Since Electric Fan Heaters are typically labeled in Wattage, you can convert the required BTU/h to Wattage to select a model:
- Required Wattage ≈ Required BTU/h / 3.41
- For example: A 200 ft² room requires 2000 BTU/h, which converts to approximately 2000 / 3.41 ≈ 587 W. Therefore, selecting an Electric Fan Heater of 750 W or higher power is appropriate.
Which Electric Fan Heater should I choose to lower my electricity bill?
The key to reducing electricity bills is not which heater is “more energy-saving” (as their energy conversion efficiency is 100%), but rather which heater can deliver heat in the smartest and most precise way.
- Choose models with the following functions:
- Precise Adjustable Thermostat: Prevents overheating.
- Timer Settings: Ensures the heater turns off when not in use.
- Multiple Power Settings: Allows the user to operate in a low Wattage mode, consuming only such as 750 W instead of 1500 W of power.
- Heating Method Choice: If you only need to quickly warm your body or a small localized area, an Infrared Electric Fan Heater is the most “efficient” choice, as it does not waste energy heating the surrounding air.
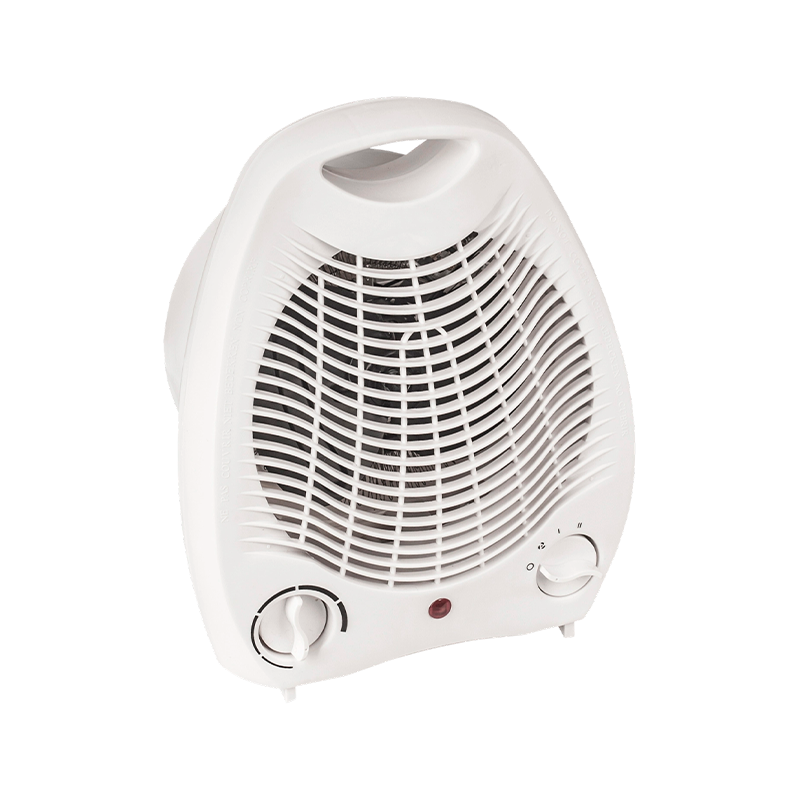 View More
FH-801-2004 best portable fan heater for home use
The FH-801-2004 Fan Heater works well in many places. It can give out warm air with two settings: 10...
View More
FH-801-2004 best portable fan heater for home use
The FH-801-2004 Fan Heater works well in many places. It can give out warm air with two settings: 10...
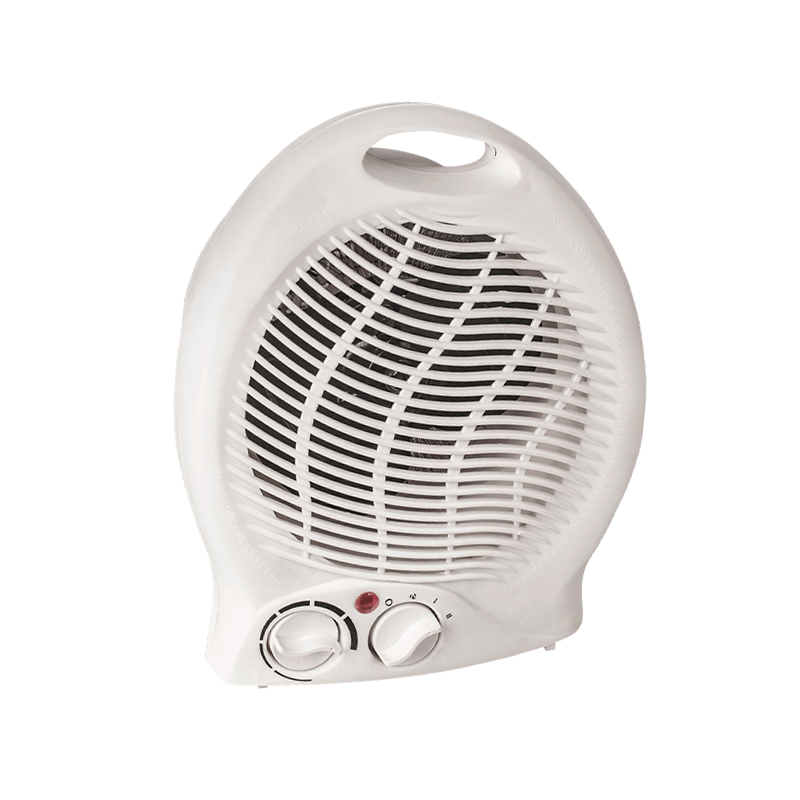 View More
HFH-801/HFH-801B small electric fan heater for personal use
This fan heater is a practical choice for everyday use. It provides warm air with 1000W and 2000W op...
View More
HFH-801/HFH-801B small electric fan heater for personal use
This fan heater is a practical choice for everyday use. It provides warm air with 1000W and 2000W op...
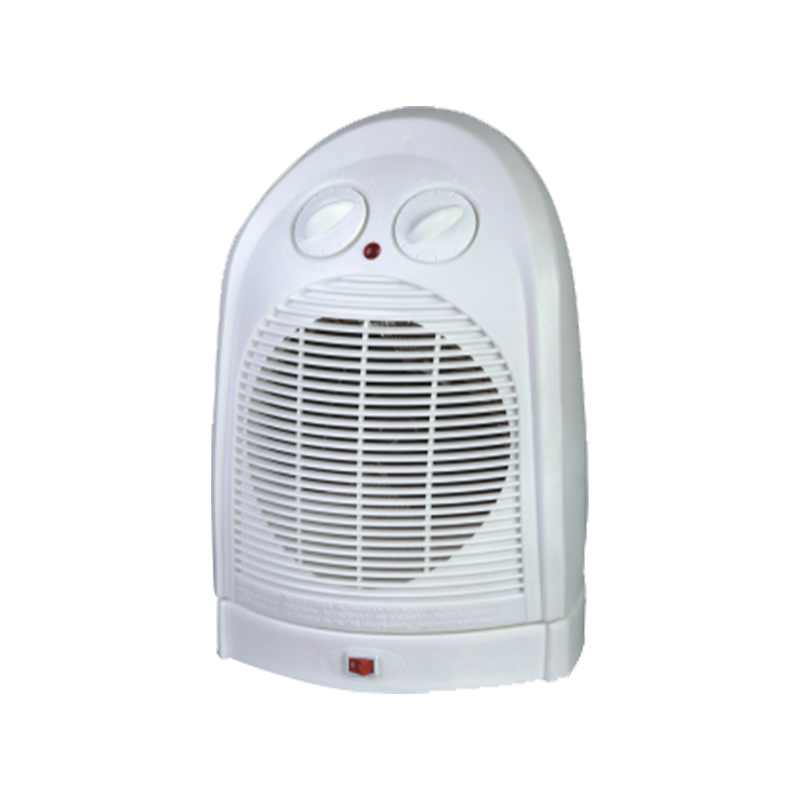 View More
HFH-806/HFH-806B energy efficient fan heater 2000w
A reliable addition to any space, this fan heater offers versatile temperature control. Choose betwe...
View More
HFH-806/HFH-806B energy efficient fan heater 2000w
A reliable addition to any space, this fan heater offers versatile temperature control. Choose betwe...
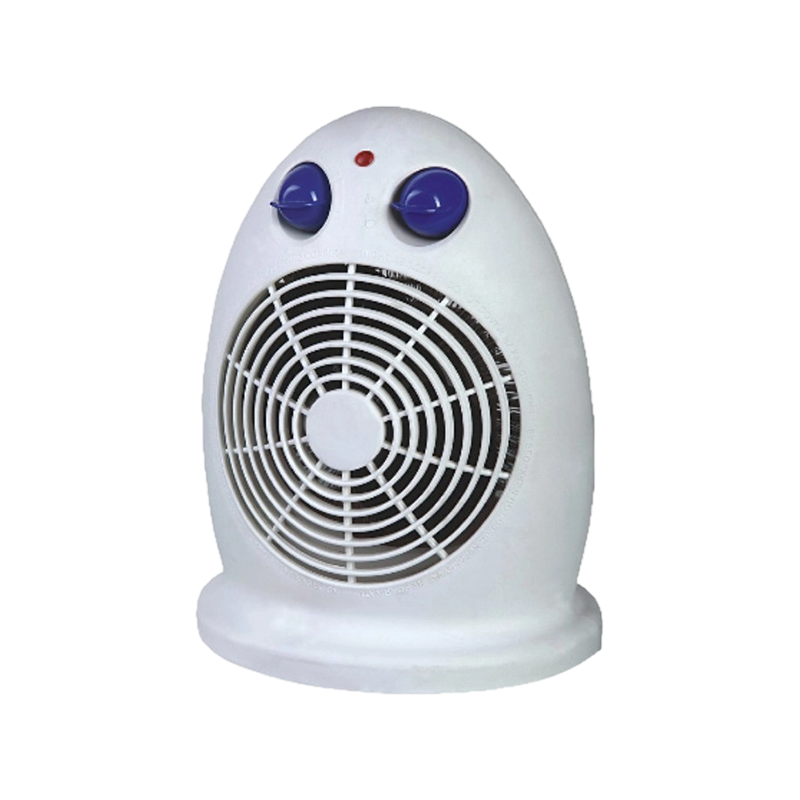 View More
FH-804 quiet mini fan heater for bedroom
Designed for everyday convenience, this fan heater delivers consistent performance. It heats with 10...
View More
FH-804 quiet mini fan heater for bedroom
Designed for everyday convenience, this fan heater delivers consistent performance. It heats with 10...
 View More
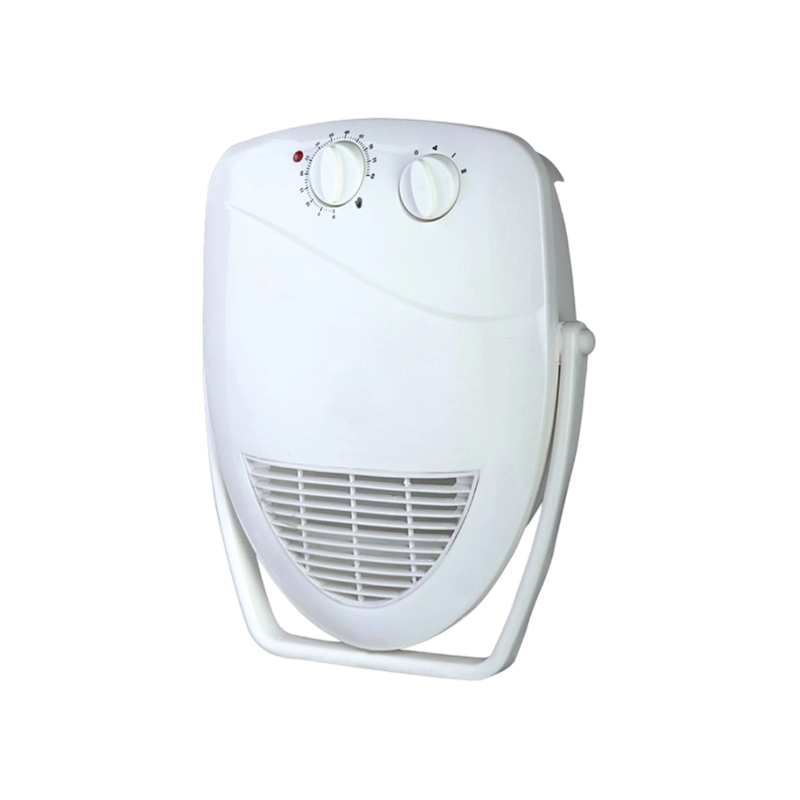
HFH-2000/HFH-2000T wall mounted fan heater with thermostat
This fan heater combines functionality with ease of use for daily comfort. With 1000W and 2000W heat...
View More
HFH-2000/HFH-2000T wall mounted fan heater with thermostat
This fan heater combines functionality with ease of use for daily comfort. With 1000W and 2000W heat...
 View More
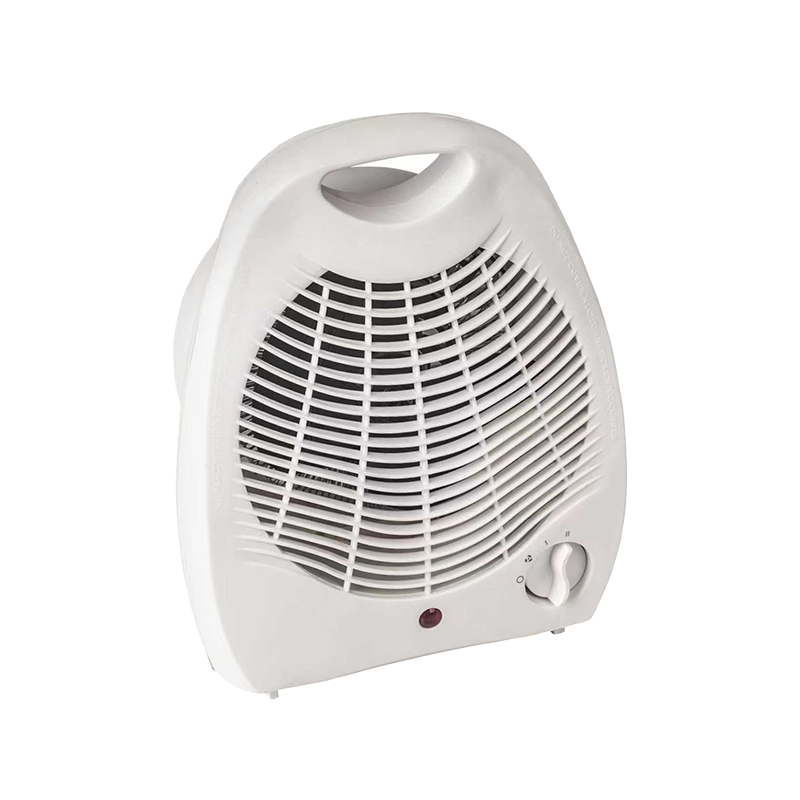
FH-801-2003 cheap portable fan heater
A straightforward and efficient fan heater, it offers 1000W and 2000W heating settings to suit varyi...
View More
FH-801-2003 cheap portable fan heater
A straightforward and efficient fan heater, it offers 1000W and 2000W heating settings to suit varyi...
 View More
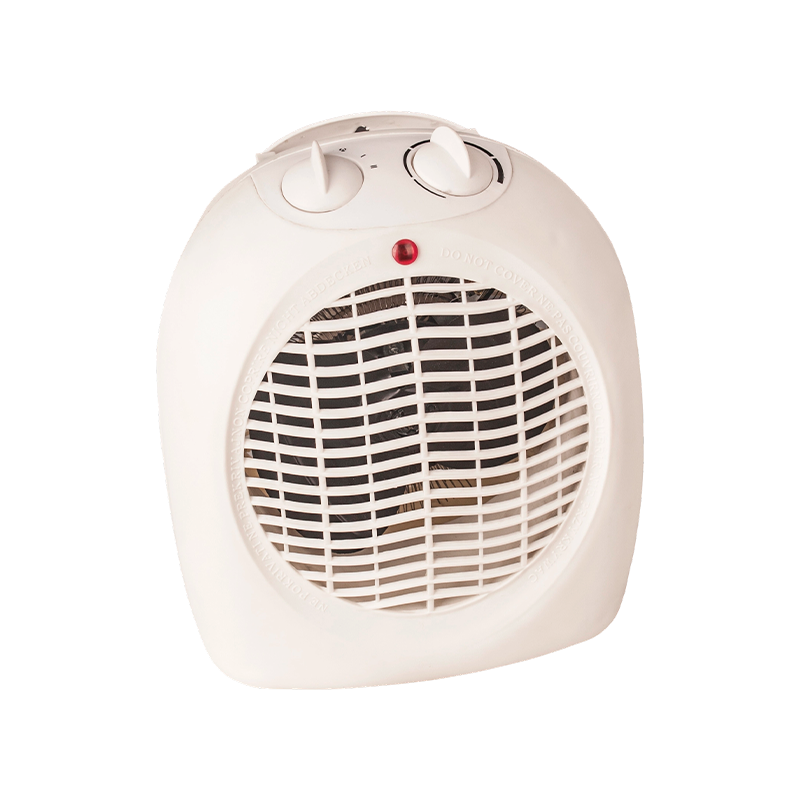
FH-303/FH-305 safest fan heater brand in Europe
This fan heater provides reliable temperature regulation for everyday use. Choose 1000W or 2000W for...
View More
FH-303/FH-305 safest fan heater brand in Europe
This fan heater provides reliable temperature regulation for everyday use. Choose 1000W or 2000W for...
 View More
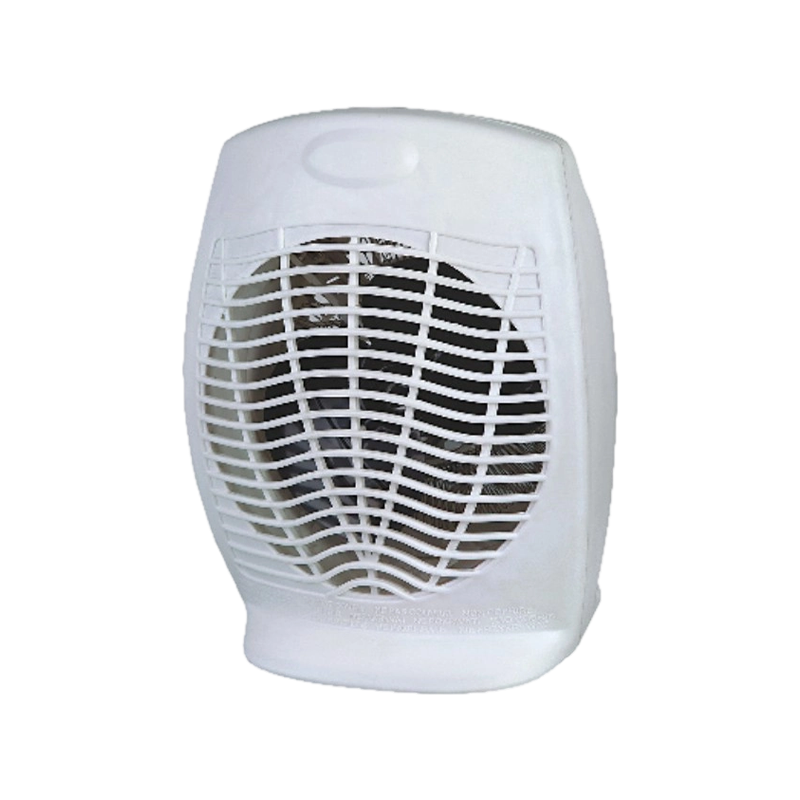
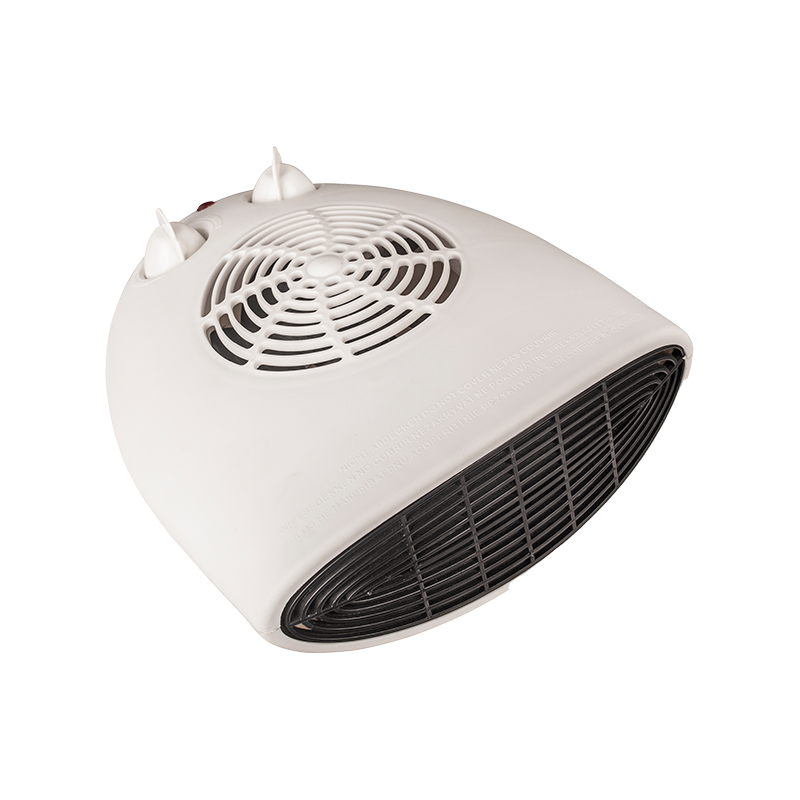
HFH-803S 2000w portable fan heater for small room
Practical and user-friendly, this fan heater offers 1000W and 2000W heating options for customizable...
View More
HFH-803S 2000w portable fan heater for small room
Practical and user-friendly, this fan heater offers 1000W and 2000W heating options for customizable...
 View More
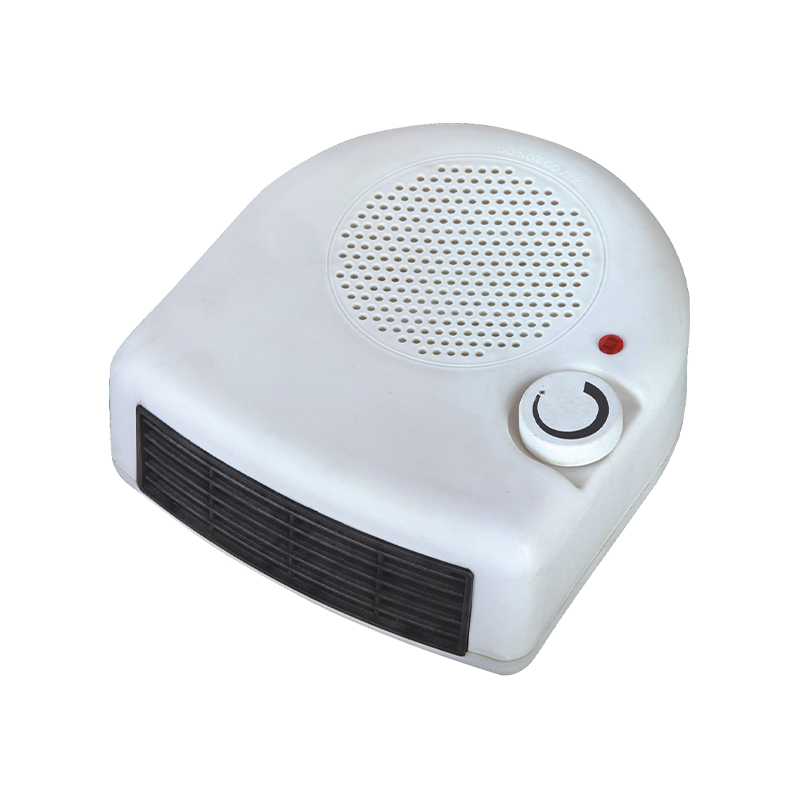
HFH-203 best fan heater for office desk
A versatile fan heater for daily use, it features 1000W and 2000W heating settings to match your com...
View More
HFH-203 best fan heater for office desk
A versatile fan heater for daily use, it features 1000W and 2000W heating settings to match your com...
 View More
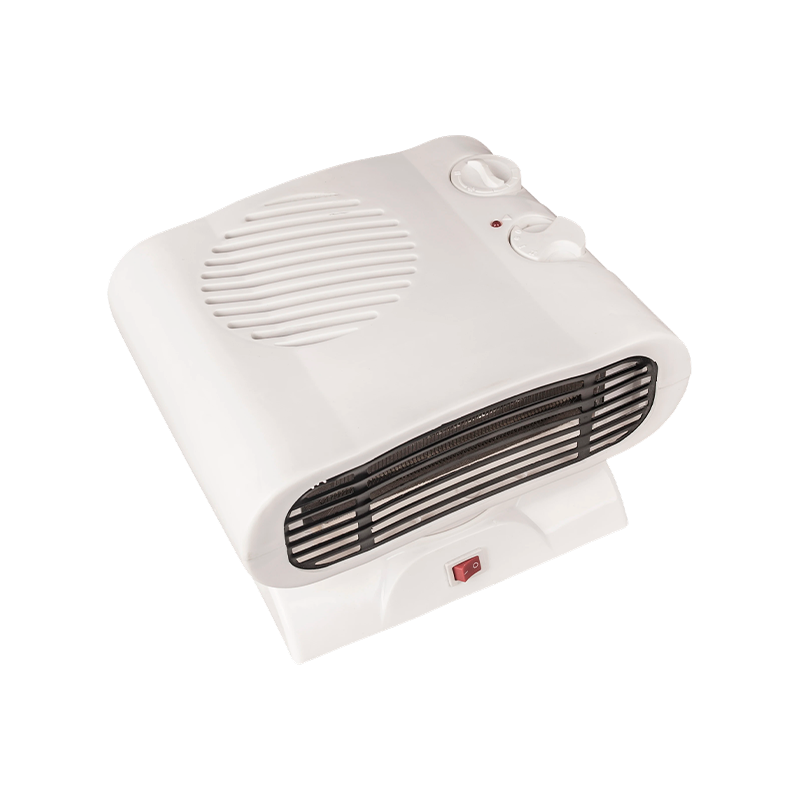
HFH-902 low energy fan heater with thermostat
This fan heater focuses on consistent performance and safety for everyday use. With 1000W and 2000W ...
View More
HFH-902 low energy fan heater with thermostat
This fan heater focuses on consistent performance and safety for everyday use. With 1000W and 2000W ...
 View More
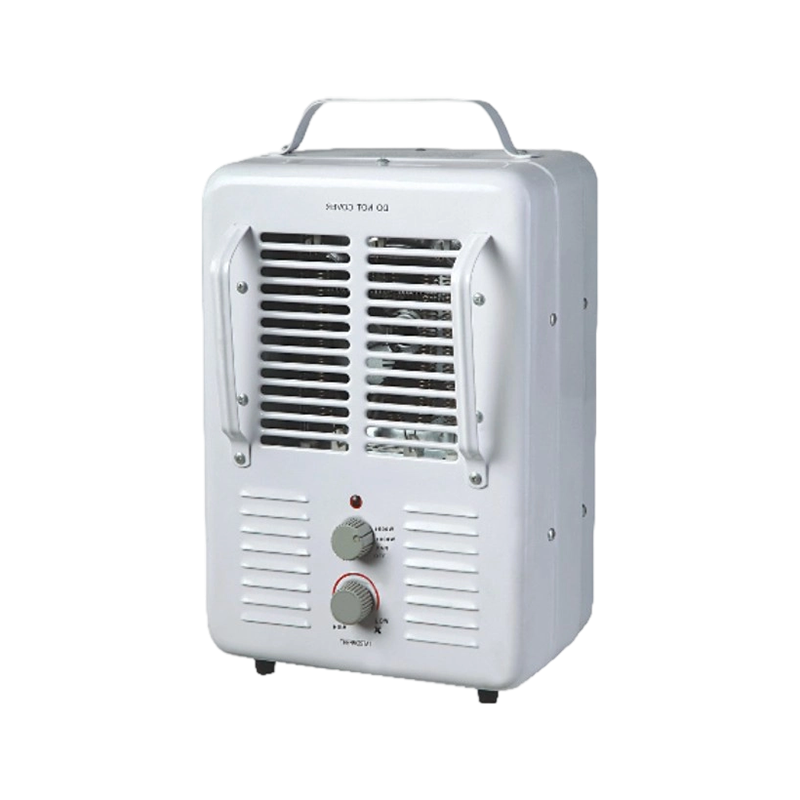
FJ-FH-01 oscillating fan heater
Designed for easy operation, this fan heater offers 1000W and 2000W heating settings to suit differe...
View More
FJ-FH-01 oscillating fan heater
Designed for easy operation, this fan heater offers 1000W and 2000W heating settings to suit differe...
 View More
FJ-FH-02 OEM fan heater with customized logo
A reliable fan heater for daily comfort, it provides 1000W and 2000W heating options for customizabl...
View More
FJ-FH-02 OEM fan heater with customized logo
A reliable fan heater for daily comfort, it provides 1000W and 2000W heating options for customizabl...




 English
English 中文简体
中文简体